Supervised Learning in Artificial Intelligence let’s chat like cafés & code
Ever wondered how machines seem to “just know” things? Like when your phone predicts the next word you’re about to type, or your email automatically filters spam like a ninja? That’s not magic, it’s supervised learning in artificial intelligence.
Let’s unpack this beast of a topic, but in a way that doesn’t make you want to throw your laptop out the window. Grab your coffee, relax, and let’s talk human-to-human (or… human-to-AI, technically).
What Supervised Learning Really Means
Picture this: you’re teaching a kid how to recognize fruits. You show them pictures of apples and bananas, and every time you tell them, “This is an apple,” or “This is a banana.” After enough examples, they can make a difference on their own.
That’s exactly how supervised learning works. It’s when an AI model is trained using labeled data, meaning each input (like a picture) comes with the correct answer (the label).
The goal? For the AI to learn patterns so it can make predictions on unseen data.
It’s called “supervised” because, just like a teacher guiding a student, we “supervise” the algorithm during training. Once it learns enough, we let it fly solo.
Why It Matters

Supervised learning isn’t just cool, it’s everywhere. From email spam filters and credit card fraud detection to self-driving cars recognizing traffic lights, this method powers much of the AI world.
Think of it as the backbone of applied artificial intelligence: practical, dependable, and super scalable when done right.
Without it, most of today’s AI systems would be like a clueless robot trying to play charades without knowing the rules.
The Two Main Types of Supervised Learning
Supervised learning comes in two main flavors: classification and regression. They might sound like terms you’d hear in a physics exam, but don’t worry, we’ll break them down like a friendly chat.
Classification Sorting Into Buckets
Classification is all about categorizing things. The model learns to assign an input to a specific class or group.
For example:
-
Is this email spam or not?
-
Is this photo of a cat or a dog?
-
Does this transaction look fraudulent?
In simple terms: if the output is a label or category, it’s a classification.
It’s like sorting laundry whites here, colors there, socks… somehow always missing one.
Regression Predicting Continuous Values

Now, regression is different. Instead of categories, it deals with numbers.
Example: predicting the price of a house, the temperature tomorrow, or a person’s weight based on their height.
If the output is a number, it’s a regression.
Think of it like this: classification says “what group does this belong to?”, while regression says “what’s the exact value?”.
Together, these two types handle most of the prediction and decision-making problems AI tackles every day.
How Supervised Learning Works (Step-by-Step)
Alright, let’s roll up our sleeves and go through the step-by-step process of how supervised learning actually works.
1. Collect and Label the Data
You can’t train what you don’t have. Data is the foundation. And labeled data? That’s gold.
Each piece of data must have a known output (a label). For example, if you’re teaching an AI to recognize cats, you’ll need thousands of labeled photos of “cat” and “not cat.”
Data labeling is often the most time-consuming and expensive part of the process. But without it, supervised learning simply doesn’t work.
2. Prepare and Clean the Data
Data isn’t perfect. It’s messy, full of duplicates, missing values, and weird outliers.
So before you feed it into the model, you have to clean it, normalize it, and make sure it’s usable. Otherwise, your model will learn garbage and give garbage results. (Yes, the old rule still applies: garbage in, garbage out.)
3. Split the Dataset
Once your data looks good, it’s time to split it into three sets:
-
Training set – the part your model learns from
-
Validation set – for fine-tuning
-
Test set – for checking how well it performs on unseen data
Think of it like preparing for an exam: you study (training), take practice quizzes (validation), and then face the final exam (testing).
4. Train the Model
Now the fun part: feeding the data into an algorithm and letting it learn.
Depending on your problem, you might use:
-
Logistic Regression
-
Decision Trees
-
Support Vector Machines (SVM)
-
Random Forests
-
Neural Networks
Each of these has pros and cons. Simple algorithms are faster to train but might be less accurate; complex ones (like neural nets) need more data and computing power.
The goal during training is to minimize the error, the difference between the model’s predictions and the actual labels.
5. Evaluate, Deploy, and Monitor
After training, you test the model using the test dataset. If it performs well, you deploy it to the real world.
But here’s the catch: your job isn’t done. Data changes over time (called data drift), and models can get outdated. You need to retrain or update them regularly.
Because, well, an AI trained on 2018 data might still think TikTok is about lip-syncing.
Estimated Cost & Resource Table
| Stage | Task | Typical Duration | Estimated Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data collection | Gather and label data | 4–12 weeks | 10,000–50,000 |
| Feature engineering | Process and clean data | 2–6 weeks | 5,000–20,000 |
| Model training | Train & tune model | 4–8 weeks | 20,000–100,000 |
| Deployment | Integration & monitoring | Ongoing | Variable |
Costs vary wildly based on project size, complexity, and available computing power.
Bottom line: supervised learning isn’t cheap, but it’s one of the most reliable methods in AI development.
Where Supervised Learning Shows Up in Real Life
Supervised learning isn’t just for researchers in lab coats. It’s already all around u, quietly running the digital world.
1. Healthcare Diagnostics
In medicine, AI systems are trained with thousands of labeled scans (like “tumor present” or “no tumor”) to detect diseases early. These systems assist doctors, speed up diagnosis, and reduce errors.
It’s like having a second opinion that never sleeps.
2. Fraud Detection in Finance
Banks use supervised learning to flag suspicious transactions. Each transaction is labeled as “fraudulent” or “legitimate,” allowing the model to detect red flags in real time.
Imagine a virtual Sherlock Holmes watching your transactions, minus the hat and pipe.
3. Marketing and Customer Behavior
Ever wondered how online stores know what you might buy next? Yup, that’s supervised learning again.
AI predicts who’s likely to make a purchase, unsubscribe, or churn. Businesses use this to personalize your experience and maybe tempt you into that “one more item” in your cart.
4. Image and Speech Recognition
Supervised learning helps AI recognize your voice, face, or photos. From unlocking phones with your face to captioning images on social media, it’s all powered by labeled data and pattern recognition.
Challenges and Limitations
Alright, before we get too dreamy about AI taking over the world, let’s be honest, supervised learning has some real-world headaches, too.
1. Labeled Data is Expensive
Gathering and labeling massive datasets takes time, people, and money. Humans need to sit and tag data, and humans make mistakes, too.
This is often the biggest bottleneck in AI projects.
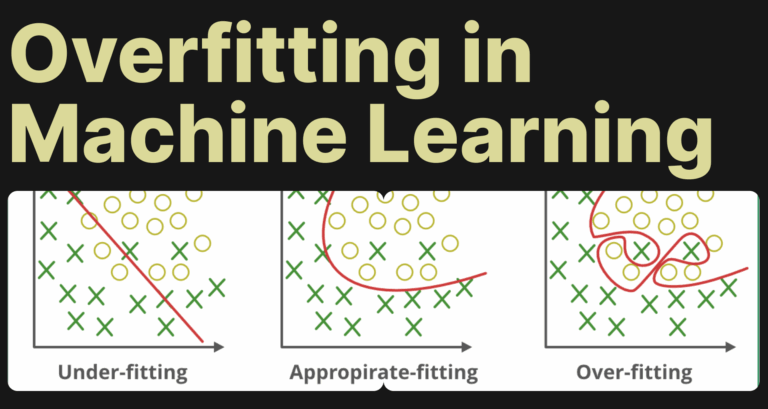
2. Overfitting and Underfitting
If a model memorizes the training data too well (overfitting), it performs terribly on new data. If it learns too little (underfitting), it misses key patterns.
Balancing the two is the secret sauce of a good model. Think of it like Goldilocks, not too simple, not too complex, just right.
3. Data Bias
If the data you feed your model is biased, your predictions will be biased too. Garbage bias in, garbage bias out.
That’s why fairness and transparency are huge parts of responsible AI today.
4. Data Drift and Maintenance
The world changes. User behavior shifts. Data evolves. Models need continuous monitoring and retraining, or they’ll slowly lose accuracy, like a singer who hasn’t practiced in years.
Best Practices for Supervised Learning
Here’s a quick list of practical do’s and don’ts if you’re planning to build a supervised learning system:
-
Start small: define one clear, measurable goal.
-
Get quality labeled data, even if it’s less, and make sure it’s accurate.
-
Use simple models first before going deep-learning-crazy.
-
Split your data properly (training, validation, testing).
-
Measure performance using the right metrics (accuracy, precision, recall, etc.).
-
Document everything: data sourcemodel versionsonand parameters.
-
Monitor continuously and retrain periodically.
-
Prioritize interpretability, know why your model makes each prediction.
Follow these and you’ll be miles ahead of most “AI experiments gone wrong.”
The Future of Supervised Learning
AI evolves fast. And supervised learning, while powerful, is also changing shape. Here’s where it’s heading next:
-
Semi-supervised learning: using small labeled datasets combined with massive unlabeled ones.
-
AutoML: automated tools that help build and tune models faster.
-
Edge AI: models that run directly on devices, not just servers.
-
Explainable AI: models that can explain their reasoning clearly.
-
Ethical AI: stronger focus on fairness, transparency, and privacy.
Supervised learning might not be the flashiest new trend, but it’s still the foundation that keeps AI practical, predictable, and profitable.
Conclusion
Supervised learning in artificial intelligence is the heart of most intelligent systems we use today. It’s how machines learn from examples, improve over time, and make decisions based on patterns.
From predicting stock prices to spotting spam emails, from diagnosing diseases to understanding speech, supervised learning quietly powers the modern world.
It’s not magic, but it’s close. The secret lies in labeled data, clever algorithms, and continuous refinement.
The more accurate and representative the data, the smarter the model becomes. But remember, supervised learning isn’t just about accuracy; it’s about responsibility, interpretability, and trust.
As AI continues to evolve, supervised learning remains the stepping stone between human knowledge and machine intelligence, where logic meets learning, and data becomes wisdom.